How to Make a ChatGPT Plugin With Python and FastAPI
ChatGPT plugins provide a new medium for developers to take advantage of OpenAI’s powerful GPT-4 model. plugins give ChatGPT access to tools via a REST API. When a plugin is installed in a user’s ChatGPT session, the model may decide to use the plugin as a part of it’s response.
You can develop plugins that enable ChatGPT to plan travel, go shopping, or do complex mathematics. In this tutorial, you’ll learn the basics of developing a ChatGPT plugin using Python and FastAPI.
This tutorial assumes you have Python and Poetry installed. For information about how to create a plugin in other languages, see:
- How to make a ChatGPT plugin with Rust
- How to make a ChatGPT plugin with Elixir
- How to make a ChatGPT plugin with Ruby on Rails
- How to make a ChatGPT plugin with Go
- How to make a ChatGPT plugin with TypeScript and Express
If you want to follow a video tutorial, you can watch the video version of this tutorial below:
Step 1: Set up the Python project
Create a new Python project with poetry by running:
poetry new python-chatgpt-pluginThis will create a project with the following directory structure:
python-chatgpt-plugin
├── pyproject.toml
├── README.md
├── python_chatgpt_plugin
│ └── __init__.py
└── tests
└── __init__.pyNext, install FastAPI and uvicorn using Poetry:
poetry add fastapi uvicorn[standard]Note: If you are on a Mac you’ll need to wrap uvicorn[standard] in quotations: "uvicorn[standard]"
Finally, activate the virtual environment by running:
poetry shellStep 2: Create the plugin API
ChatGPT interacts with plugins via a defined REST API. You can quickly create a REST API in Python using FastAPI. First, create a new file in the python_chatgpt_plugin folder called main.py. Then, add the following code to the file:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI(
title="Python ChatGPT plugin",
description="A Python ChatGPT plugin"
)
@app.get("/hello", description="Says hello from the ChatGPT plugin")
async def hello():
return {"message": "Hello from the plugin!"}This code creates a new FastAPI application and adds a single GET route at the path /hello. The /hello route will return a JSON object with the given message from the plugin. Notice the description argument in the route describes the action the given route will take when called. It’s important to make these descriptive, as it provides context to the model to decide what action to take when using your plugin.
Step 3: Set up CORS middleware for development
In order to test your plugin locally before deploying to production, you need to configure your application to allow Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) from the ChatGPT website. CORS enables ChatGPT to request access to resources from your locally running webserver. To setup CORS with FastAPI, you can use the CORSMiddleware:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
app = FastAPI(
title="Python ChatGPT plugin",
description="A Python ChatGPT plugin"
)
# Enable CORS for https://chat.openai.com/
app.add_middleware(
CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=["https://chat.openai.com"],
allow_credentials=True,
allow_methods=["*"],
allow_headers=["*"],
)
@app.get("/hello", description="Says hello from the ChatGPT plugin")
async def hello():
return {"message": "Hello from the plugin!"}CORSMiddleware will configure CORS for your application from https://chat.openai.com.
Step 4: Create the plugin manifest
Every ChatGPT plugin must ship with a plugin manifest hosted on the same domain as the API. ChatGPT looks for the plugin specifically at the path /.well-known/ai-plugin.json. You can read more about the specifics of the plugin manifest in our What is the ChatGPT plugin manifest? post.
For your plugin, start by creating a new file in your plugin directory called ai-plugin.json. Next, add the following:
{
"schema_version": "v1",
"name_for_human": "My First plugin",
"name_for_model": "pythonPlugin",
"description_for_human": "My first ChatGPT plugin",
"description_for_model": "plugin which says hello.",
"auth": {
"type": "none"
},
"api": {
"type": "openapi",
"url": "http://localhost:8000/openapi.json",
"is_user_authenticated": false
},
"logo_url": "http://localhost:8000/logo.png",
"contact_email": "support@example.com",
"legal_info_url": "http://www.example.com/legal"
}In this example, the “auth” field is set to “none” because this plugin doesn’t require authentication. However, depending on your use case, you might need your plugin to handle authentication. For more information about how to implement authentication in a ChatGPT plugin, you can refer to our ChatGPT Plugin Authentication Guide.
Next, add a route for accessing the plugin manifest from your app:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
import json
app = FastAPI(
title="Python ChatGPT plugin",
description="A Python ChatGPT plugin"
)
# Enable CORS for https://chat.openai.com/
app.add_middleware(
CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=["https://chat.openai.com"],
allow_credentials=True,
allow_methods=["*"],
allow_headers=["*"],
)
# Load and serve the plugin manifest
with open('ai-plugin.json', 'r') as manifest_file:
manifest_content = json.load(manifest_file)
@app.get("/.well-known/ai-plugin.json")
async def serve_manifest():
return manifest_content
@app.get("/hello", description="Says hello from the ChatGPT plugin")
async def hello():
return {"message": "Hello from the plugin!"}And that’s all you need!
Step 5: Install and test your plugin
First, start your plugin server locally by running:
uvicorn python_chatgpt_plugin.main:appYou can verify it worked by navigating to http://localhost:8000/docs in your browser:
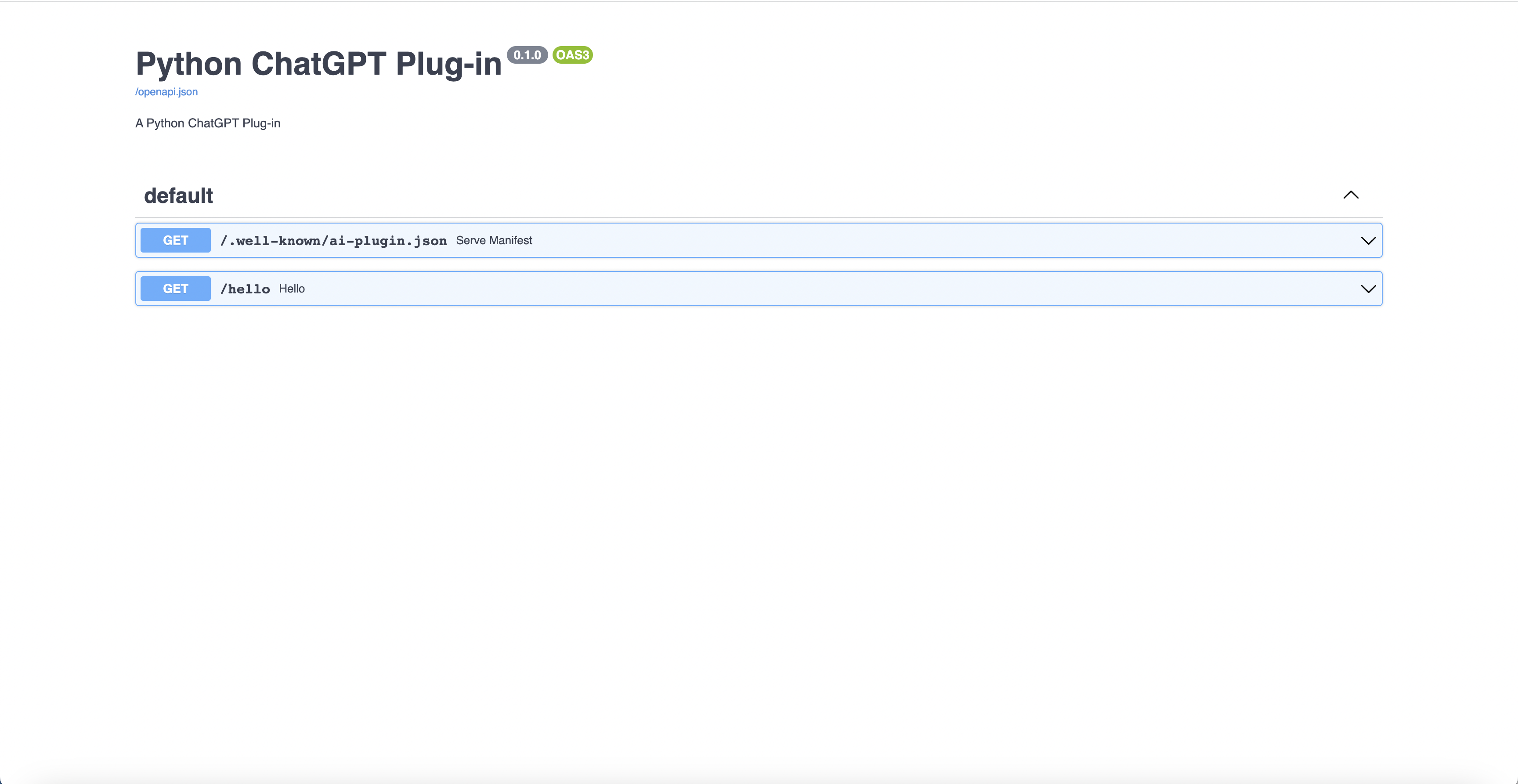
Next, navigate to the ChatGPT UI and select the plugin model:

Then, you’ll want to select the plugins dropdown, navigate to the plugin store, and click “Develop your own plugin” in the bottom right:

Finally, type your localhost URL into the plugin form:
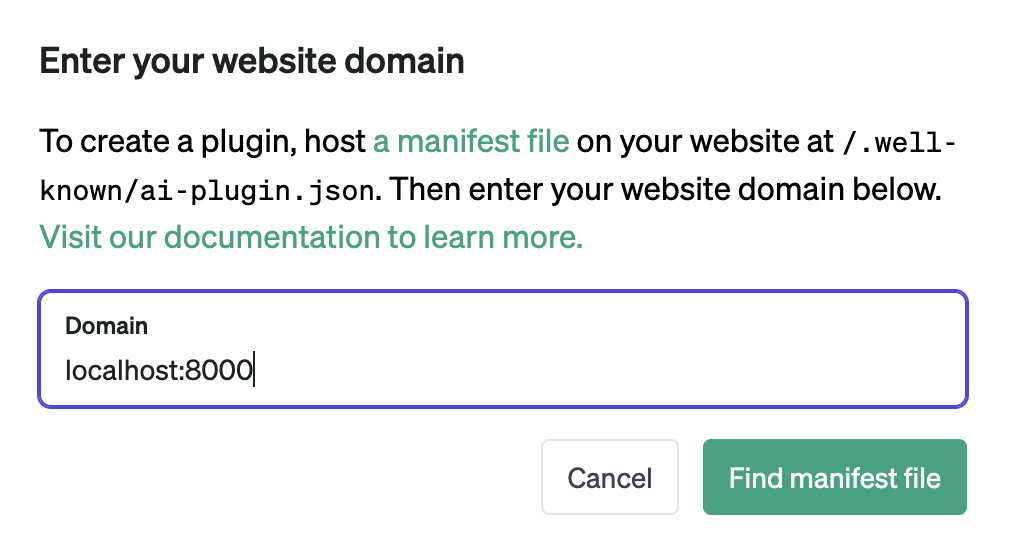
After awhile, you’ll see the following:
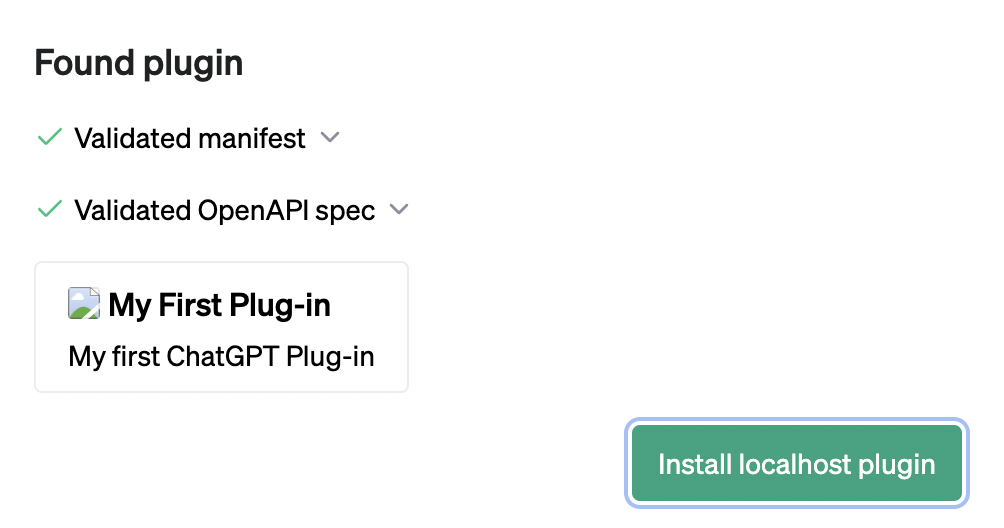
Click “Install localhost plugin” to continue. With your plugin enabled, you can start to interact with it using ChatGPT. For example, try typing in “Say hello from my plugin” into the chat window:
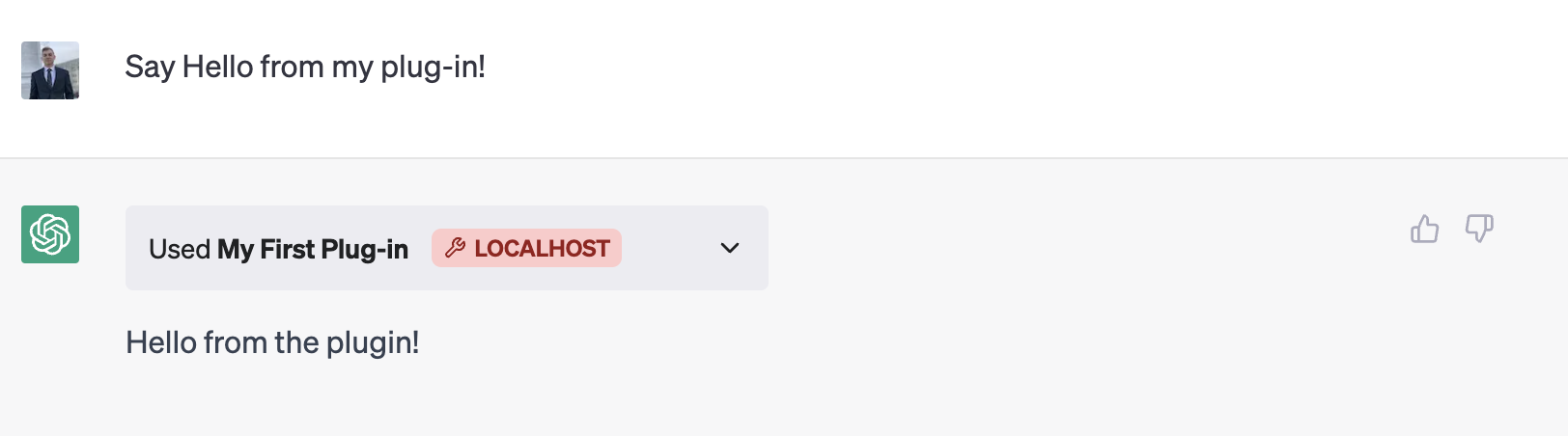
Congratulations! You’ve successfully made your first ChatGPT plugin with Python and confirmed it works locally. Next, check out our deployment and hosting guide to learn about deploying your plugin to production.
Enjoyed this post?
Subscribe for more!
Get updates on new content, exclusive offers, and exclusive materials by subscribing to our newsletter.